Although asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood, it can also develop in adults, even in later life. Asthma affects more than 6 million children (see also Asthma in Children) in the United States and occurs, most frequently, in prepubescent boys and girls after puberty. Eventually, asthma may resolve in children. However, asthma that appears to resolve sometimes reappears years later. It also develops with a higher incidence in non-Hispanic black and Puerto Rican populations. Although the number of people with asthma has increased, the number of deaths has declined.
The most important feature of asthma is a reversible narrowing of the airways. The intrapulmonary airways (bronchi) are, essentially, tubes with muscular walls. The cells lining the bronchi possess microscopic structures called receptors. These receptors sense the presence of specific substances and stimulate the underlying muscles to contract or relax, thus altering the flow of air. There are many types of receptors, but there are mainly two that are important in asthma: the Beta-adrenergic receptors are sensitive to chemicals such as epinephrine and result in muscle relaxation, opening (dilating) the airways and increasing flow; instead, the Cholinergic receptors respond to a chemical called acetylcholine, activate muscle contraction, and thereby reduce flow.
Causes of Asthma
The causes of asthma are unknown, but asthma is likely the result of interactions between many factors, from the circumstances surrounding pregnancy and birth to environmental conditions and nutrition.
In the case of pregnancy, the risk seems greater if the mother of a person with asthma became pregnant at a young age, or had malnutrition during pregnancy; even in the case of prematurity, low birth weight or artificial breastfeeding, the risk of contracting the disease seems greater. Coming to environmental conditions, such as exposure to household allergens (pollen, particles from dust mites, cockroach secretions, particles from animal feathers and hair) and other environmental allergens, have been associated with the development of asthma in older children and adults. Nutritionally, diets low in vitamins C and E and omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to asthma, as has obesity; however, there is no evidence that dietary supplements of these substances can prevent the development of asthma.
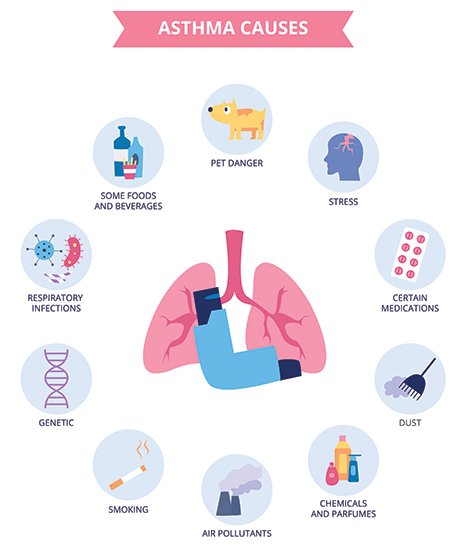
In general, airway narrowing in an asthmatic person occurs in response to stimuli (triggers) that usually do not affect nonasthmatic people. These triggers include the main ones: allergens, infections, irritants, exercise (referred to as exercise-induced asthma), stress and anxiety, and aspirin. Infectious triggers are, generally, viral respiratory infections: colds, bronchitis, and, less commonly, pneumonia.
Symptoms of Asthma
When a person suffers from asthma, he or she experiences symptoms such as:
more or less persistent wheezing cough, which may appear or become more pronounced during the nighttime hours or upon awakening, sometimes associated with a sense of stuffy nose or repeated sneezing; difficulty breathing or dyspnea (shortness of breath); breathing is wheezing, although this feature is not always perceived by the patient.
All these symptoms do not occur at the same time in the same person, nor do they always occur with the same intensity (when they are very intense we also speak of an asthma crisis) and can develop at different times, throughout life.
In order to proceed with an early diagnosis, if the above-mentioned symptoms (coughing, shortness of breath and wheezing) occur, investigations should be performed. Although asthma mainly affects young people, it can occur at any age; after the age of 30, it mainly affects women, tends not to have an allergic origin and responds poorly to drug therapy.
You may also like
Hearing loss: things to know before buying a hearing aid
Choosing a hearing aid isn’t easy, especially if you’ve never used one. They come in different shapes, colors and levels of technology.The first factor in determining which hearing aid to choose is your hearing loss, which could range from very mild to severe. Next, you need to know what you would like it to be… Continua a leggere Hearing loss: things to know before buying a hearing aid
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Symptoms and Treatments, Causes and Diagnosis
Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) is a cancer of the immune system. It affects infection-fighting white blood cells called B cells. SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which along with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) indicates the same type of disease, treated the same way. Whereas in SLL, the cancer cells reside primarily in the lymph… Continua a leggere Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Symptoms and Treatments, Causes and Diagnosis
Diabetes Type 2: Epidemiology and Prevention
Diabetes Epidemiology Diabetes is a very common disease. New updated data from the new International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas show that more than 34 million Americans have diabetes (1 in 10 individuals), of whom approximately 90-95% have type 2 diabetes. In UK the situation is slightly better: with nearly 4 million sufferers, about one… Continua a leggere Diabetes Type 2: Epidemiology and Prevention
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Stats, Causes and Diagnosis
Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) is a cancer of the immune system that affects the white blood cells that fight infection, called B cells. SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, as is chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Both cancers are basically the same disease, and are treated in almost the same way. The difference between the… Continua a leggere Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Stats, Causes and Diagnosis
