In case of acute hepatitis C infection most of the people are asymptomatic, so they show no signs of infection. Symptoms of hepatitis C usually show up within two weeks, at most six months after exposure to the virus.
Which are Hepatitis C Symptoms?
They resemble you have mild symptoms of the flu: tiredness, muscle pain, joint pain, fever, lack of appetite, stomach pain, itchy skin, dark colored urine and slight jaundice (yellow skin and whites of the eyes). In most cases (70-80%) the evolution of acute hepatitis C into chronic hepatitis C means that, beyond the totally missing symptoms, the virus infection is in progress; in other words, it can last 15 years or more before it is actually diagnosed.
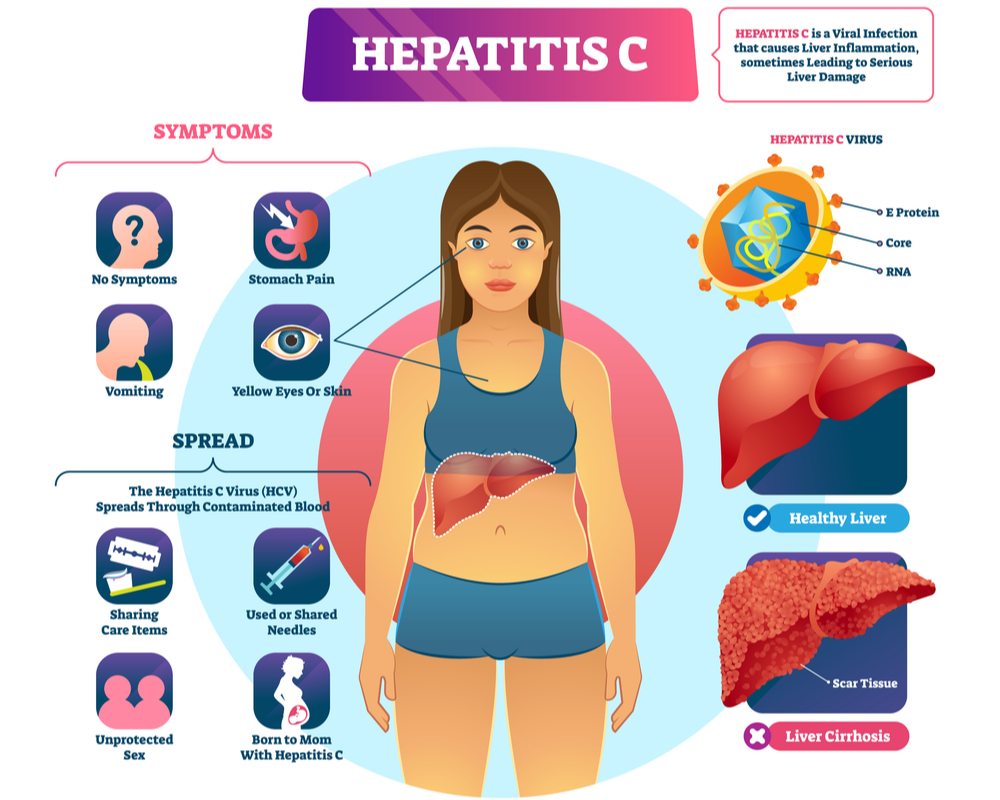
How is Hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is only transmissible through the blood, that is when the bloodstream of an infected person comes into contact with that of a healthy person. In most cases, this happens while using needles to inject substances into the bloodstream (drugs or medications). Until 1992, in the United States, blood and organ screening was not standard, so it is believed that the disease was quite widespread in the medical health sector, thanks to blood transfusions or organ transplants. Unlike the common cold, Hepatitis C is not that contagious, therefore it is not possible to be infected through kissing, hugging, sneezing, coughing, holding hands or sharing food, drinks and utensils.
Diagnosis
As recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, for all adults between the ages of 18 and 79, screening for hepatitis C is recommended, and especially for those at-risk categories mentioned in our previous Hepatitis C article. If the first phase of screening, carried out through a first blood test, shows that the positivity to the HCV virus, further blood tests are necessary, able to measure the viral load present and identify the genotype of the virus.
Having ascertained the significant presence of the HCV virus in the body, in order to assess the liver damage caused by chronic hepatitis C, doctors resort to even more in-depth tests. Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE): This is a less invasive approach than liver biopsy, which combines magnetic resonance technology with patterns formed by sound waves. By bouncing off the liver, the sound waves create a visual map showing the various levels of stiffness; portions of stiff liver tissue indicate the presence of fibrosis due to chronic hepatitis C. Transient Elastography: with a type of minimally invasive ultrasound, vibrations are transmitted to the liver to estimate its rigidity, by measuring the speed of dispersion in the liver tissue. Liver biopsy: This test involves inserting a fine needle through the abdominal wall to remove a small sample of liver tissue for laboratory testing. Blood tests: Series of blood tests can indicate the extent of fibrosis in the liver.
Prevention
If you are not positive for the HCV virus, reducing the risk of contraction is possible. Here are some practical tips, for particular cases.
If you use drugs by injection, find out about a treatment program and, in the meantime, avoid sharing needles (or other appliances) with third parties (in many cities, there are programs for providing sterile replacement needles). If you are undergoing a piercing or tattoo, check that all the equipment has been properly sterilized. If you are a healthcare professional, just follow the safety precautions:. Wear protective clothing and gloves, properly dispose of contaminated sharp objects. If you have more than one sexual partner or are a man who has sex with other men, use condoms for intercourse.
You may also like
Hearing loss: things to know before buying a hearing aid
Choosing a hearing aid isn’t easy, especially if you’ve never used one. They come in different shapes, colors and levels of technology.The first factor in determining which hearing aid to choose is your hearing loss, which could range from very mild to severe. Next, you need to know what you would like it to be… Continua a leggere Hearing loss: things to know before buying a hearing aid
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Symptoms and Treatments, Causes and Diagnosis
Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) is a cancer of the immune system. It affects infection-fighting white blood cells called B cells. SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which along with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) indicates the same type of disease, treated the same way. Whereas in SLL, the cancer cells reside primarily in the lymph… Continua a leggere Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Symptoms and Treatments, Causes and Diagnosis
Diabetes Type 2: Epidemiology and Prevention
Diabetes Epidemiology Diabetes is a very common disease. New updated data from the new International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas show that more than 34 million Americans have diabetes (1 in 10 individuals), of whom approximately 90-95% have type 2 diabetes. In UK the situation is slightly better: with nearly 4 million sufferers, about one… Continua a leggere Diabetes Type 2: Epidemiology and Prevention
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Stats, Causes and Diagnosis
Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) is a cancer of the immune system that affects the white blood cells that fight infection, called B cells. SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, as is chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Both cancers are basically the same disease, and are treated in almost the same way. The difference between the… Continua a leggere Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): Stats, Causes and Diagnosis
